Types of Network Switches
17 Oct, 2022.
In this post, we will see the various types of network
switches used in automaton and networking.
Network is a very basic system used everywhere, right from our home to commercial applications to large industrial applications. With growing business and data flow, communication networking has become a very pivotal component in playing it’s role. For networking, you need to have knowledge of Ethernet network switches, which are used for data routing and transfer. You must know which network has been created by which type of switch, and how it is working. So, understanding various types of them is a must. In this post, we will see the most general types of network switches used.
What is a network switch?
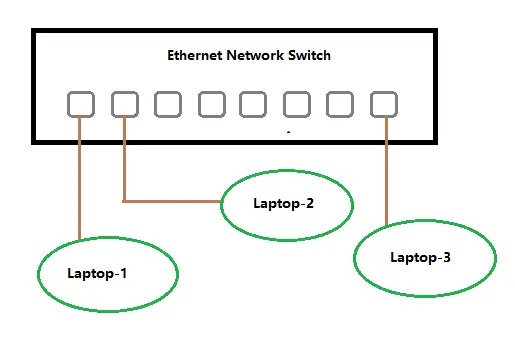
There are times when you require to connect multiple network devices like computers, cameras etc. together, for data routing and transfer. In this case, a network switch is used, which binds all these devices together. It identifies which device is connected on which port, by identifying it’s MAC address. Data is transferred only to the device for which it is destined. It will not go to any other device. If you have a lot of wired devices and you want to create a network with all of them, then a network switch is used for this purpose. So, it can simply be defined as a bridge connecting two network devices. Refer the below image for understanding more properly.
Types of network switches:
1. Desktop switch:
It is a category based on data transfer size. This is the normal Ethernet extension switch that we use in our daily use or small-scale applications. For example, suppose you want to communicate three laptops with each other, then use a 5-port switch. Connect LAN cables to the three laptops with this port. The laptops will communicate with each other. It is available in 4-port, 8-port or 16-port. It is best for small scale applications. It can transfer data up to 100 mbps.
2. Giga switch:
It is a category based on data transfer size. For data above 100mbps, you will need a Giga switch. If you use a normal desktop switch, then the data communication will lag and there are high chances of data getting skipped frequently. You can use this switch for data transfer of up to 1000 mbps. Suppose there are two data networks having data of 128 mbps each. Then, using this switch by connecting both these networks to it, you can transmit and receive data easily.
3. Unmanaged switch:
It is a category based on security. It is called unmanaged switch, because you do not need any configuration for it. Just plug and network your devices without any configuration, which means there is no management in the network. Because there is no management, there is no security cover for the network devices connected in it.
4. Managed switch:
It is a category based on security. As the name implies, you can manage each port of the switch through the device manufacturer’s software. Once you login in the software, you can do various settings like device description, IP address, IP address mode (Static IP, DHCP, and BOOTP), LAN ID, access control, multicast, QoS (quality of service), SNMP, cluster, and maintenance. Because of this, you can secure and manage the connection of devices to it.
5. POE (Power Over Ethernet) switch:
In this cable, if you plug in the Ethernet cable from the switch to a device, then that device will be powered up. The device is typically a router or gateway switch. It is the most used nowadays, as it reduces additional power supply wiring. The LAN port itself is configured in such a way that it will power up the device connected through it. Be sure to check if your PoE switch is compliant with the 802.3af/at standard and if the device you want to connect can support that.
6. Switches with optical fiber ports:
A standard cat6 cable can be extended up to a maximum distance of 100m. Beyond that, optical fiber protocol is used to boost up communication distance. So, there are network switches which additionally come with fiber optics ports (SFP – small form factor pluggable) for connecting to fiber optics cables.
7. Layer 3 switches:
It is a category based on OSI layer network. In layer 2 (the
general ones we use), you can send data to the same subnet and gateway address
devices. For example, you have a PC with IP address 192.168.1.20; and you want
to send data to a PC with IP address 192.168.1.30. The gateways are common with
192.168.1.1. Here, you can use layer 2 switches. But if you need to send data
to a PC with IP address 192.52.0.2, which is of different subnet and gateway,
then you need to use layer-3 category (L3) switches. Their software is
more advanced from pure Layer2 switches, and they can run dynamic routing
protocols such as RIP, OSPF etc. If there is a need of communication
between different VLANs in the network, traffic flows from the lower Layer 2
switches through the core Layer 3 switch which routes the packets from one VLAN
to another.
I have covered the general types of network switches used in
IT and networking. I have also not attempted to cover every theory of
these types deeply; you can learn it easily once you get familiar with them. I
have just given you an insight of these types of switches. Once you are done
with these, I am hopeful you will be easily able to understand any switch
properly. Learn the basics and explore a new type of study in this type of
engineering. It will take some practice and as you go on studying the switches,
you will become more familiar with it.
Thank you, guys; I hope you enjoyed reading the practices normally used for this type of study in industrial automation.



Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any queries, please let me know